As it stands today, nanotechnology on a global scale is set to transform and revolutionize business. A Business Wire report confirmed that the global nanotechnology market is poised to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.1% over the next ten years to a market size of $173.95 billion by 2025. Nano tech is going to have technological breakthroughs and advancements for the different branches in medicine. Particularly, the implementation of nanotechnology in dentistry will transform the business end of it, the profession, and how the materials are utilized to treat patients in the future. As a result, we have nanodentistry. It is the science and technology of diagnosing, treating and preventing oral or dental diseases. In addition, it is enhancing the dental health through nanostructured materials. Contrary to popular belief there is a huge business component to dentistry. Becoming a licensed dentist is a rigorous process—years of study and a demanding amount of time investment in learning the profession. But there is an entrepreneurial aspect to this profession. A licensed dentist or dental professional must oversee the payroll, hiring, terminating and attracting enough patients’ business operations.[2] From the early 1990s, nanotechnology has been exploited for medical and dental applications. This new form of nanodentistry has more than the potential to improve oral health. This would be possible thanks to the sophisticated, preventive, diagnostic and therapeutic measures of nanomaterials, biotechnology and nanorobot, as reported by the Journal of Orofacial Sciences. Aspects of the profession will undergo a transformation. For example, the dental materials typically used for routine dental procedures may see combinations that include nanodiamonds, (which will discussed in the next section).
Adoption of nano dental materials and barriers to entry
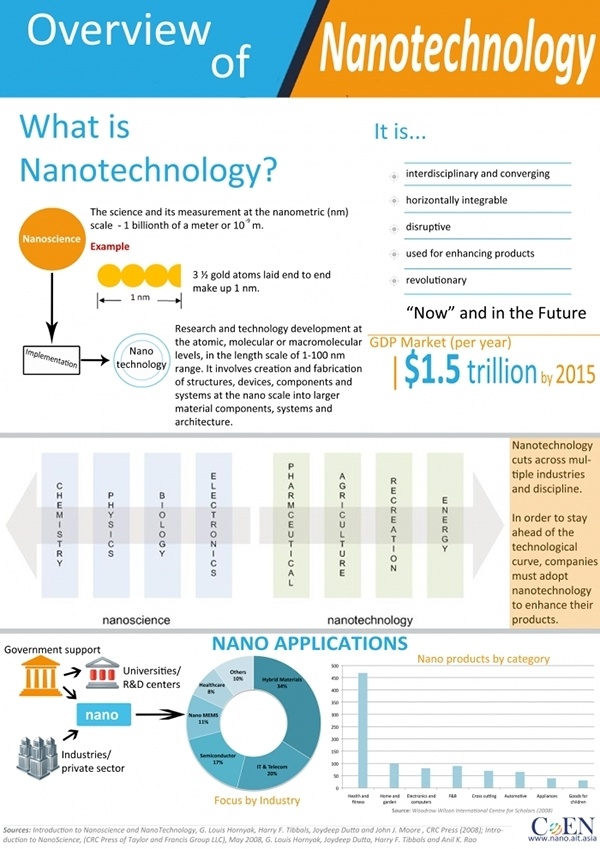
Taking a step back, we now know nanotechnology is a science and its measurements at the nanometric scale, but just how much does it represent for gross domestic product (GDP)? The following infographic is an overview of nanotechnology and how much of the GDP it is:
The GDP of nanotechnology represented $1.5 trillion in 2015. So this nanotechnology cuts across multiple industries and different disciplines. That said, over the next five to ten years, adopting this technology remains pivotal for those in this sector of healthcare. What has been a recent novelty of nanotechnology is the enhancement properties and benefits it will bring to dentistry. As illustrated by a Forbes.[3] As explained by Guardian Dental, nanotechnology brings with it a promising future. On the other hand, there are hurdles to overcome with regards to safety and cost barriers before it completes its introduction across the marketplace. Phys.org asserts it will not just help the creation of the next generation of dental materials. Since its introduction a decade earlier, engineers have been developing what materials can be used at a dental office. One strong possibility could include products like antimicrobial adhesives, which is made of nanotubes and could create a sort of a wearable toothpaste amongst other plausible nanodental materials. Naturally some of the components or, in this case, the composition can be toxic to healthy living cells. There is still plenty of research to be conducted, pre-clinical and clinical trials to test the safety of nanomaterials. Once approved, the scientific community can work with these dental-enhancing nanomaterials. The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) published a detailed journal on the present and future of nanotechnology in dentistry. These are additional challenges nanotechnology faces: “Precise positioning and manufacture of nanoscale parts.” “Cost-effective nanorobot mass manufacturing methods.” “Financing and tactical concerns.” “Inadequate assimilation of clinical research.” Social issues of public acceptance, ethics, regulation and human safety.” The precise positioning and manufacturing of nanomaterials is still in its infancy stages. How it gradually gets introduced will largely depend on the government’s ability to offer subsidies combined with private capital funding. Furthermore, its general acceptance into this branch of medicine. Where the financing will come from will be a combination of public and private institutions. This will be subject to resistance, debate and even rejection. And the biggest hurdle is the public acceptance of it and how to carry out clinical trials on actual human beings. Before it clears approval it will be subject to regulation and will have to clear most safety concerns associated with it.
Takeaways and conclusions
Nanotechnology is set to grow substantially over the next decade. The technology will usher new nanocomposite dental materials that endure for long periods of time and effectively remedy dental diseases. Nanotechnology is already creating a revolution within healthcare, reshaping the disciplines as we speak. Infographic credit via balance.net Featured photo credit: Matthias Weinberger via Flickr via flickr.com